The perpendicular line that is drawn at right angles to a reflecting surface at the point of incidence.
End of chapter exercises
|
Previous
5.8 Summary
|
Next
6.1 Introduction
|
End of chapter exercises
Give one word for each of the following descriptions:
The bending of light as it travels from one medium to another.
The bouncing of light off a surface.
State whether the following statements are true or false. If they are false, rewrite the statement correcting it.
The refractive index of a medium is an indication of how fast light will travel through the medium.
Total internal refraction takes place when the incident angle is larger than the critical angle.
The speed of light in a vacuum is about \(\text{3} \times \text{10}^{\text{8}}\) \(\text{m·s$^{-1}$}\).
Complete the following ray diagrams to show the path of light.
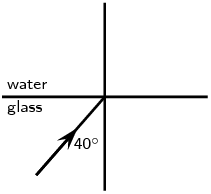
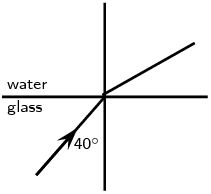
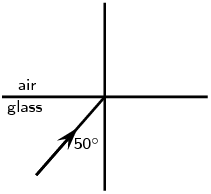
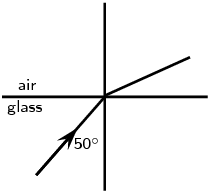
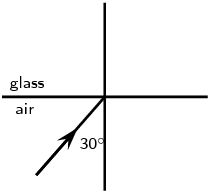
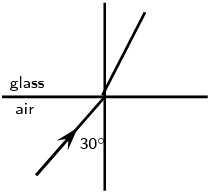
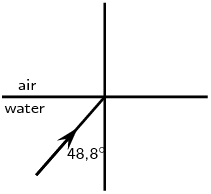
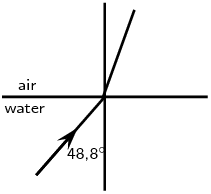
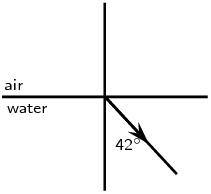
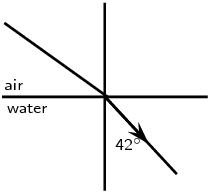
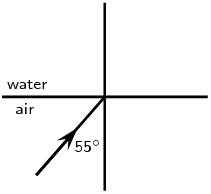
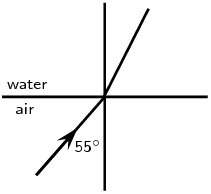
A ray of light strikes a surface at \(\text{35}\)\(\text{°}\) to the normal to the surface. Draw a ray diagram showing the incident ray, reflected ray and surface normal. Calculate the angles of incidence and reflection and fill them in on your diagram.
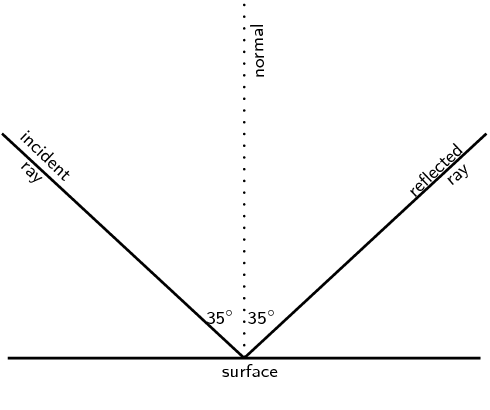
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. This angle is \(\text{35}\)\(\text{°}\).
Light travels from glass (\(n = \text{1,5}\)) to acetone (\(n = \text{1,36}\)). The angle of incidence is \(\text{25}\)\(\text{°}\).
Describe the path of light as it moves into the acetone.
The light bends towards the normal.
Calculate the angle of refraction.
What happens to the speed of the light as it moves from the glass to the acetone?
The speed of light increases.
What happens to the wavelength of the light as it moves into the acetone?
The wavelength of the light increases.
Light strikes the interface between diamond and an unknown medium with an incident angle of \(\text{32}\)\(\text{°}\). The angle of refraction is measured to be \(\text{46}\)\(\text{°}\). Calculate the refractive index of the medium and identify the medium.
The substance is sapphire.
Explain what total internal reflection is and how it is used in medicine and telecommunications. Why is this technology much better to use?
Total internal reflection takes place when light travels from one medium to another of lower optical density. If the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle for the medium, the light will be reflected back into the medium. No refraction takes place.
Optical fibres are most common in telecommunications, because information can be transported over long distances, with minimal loss of data. This gives optical fibres an advantage over conventional cables. Signals are transmitted from one end of the fibre to another in the form of laser pulses. A single strand of fibre optic cable is capable of handling over \(\text{3 000}\) transmissions at the same time which is a huge improvement over the conventional co-axial cables. Multiple signal transmission is achieved by sending individual light pulses at slightly different angles. The transmitted signal is received almost instantaneously at the other end of the cable since the information coded onto the laser travels at the speed of light! During transmission over long distances repeater stations are used to amplify the signal which has weakened by the time it reaches the station. The amplified signals are then relayed towards their destination and may encounter several other repeater stations on the way.
Optic fibres are used in medicine in endoscopes. The main part of an endoscope is the optical fibre. Light is shone down the optical fibre and a medical doctor can use the endoscope to look inside the body of a patient. Endoscopes can be used to examine the inside of a patient’s stomach, by inserting the endoscope down the patient’s throat. Endoscopes also allow minimally invasive surgery. This means that a person can be diagnosed and treated through a small incision (cut). This has advantages over open surgery because endoscopy is quicker and cheaper and the patient recovers more quickly. The alternative is open surgery which is expensive, requires more time and is more traumatic for the patient.
|
Previous
5.8 Summary
|
Table of Contents |
Next
6.1 Introduction
|
