6.3 Huygens' principle
|
Previous
6.2 Wavefronts
|
Next
6.4 Diffraction
|
6.3 Huygens' principle (ESBNG)
Christiaan Huygens described how to determine the path of waves through a medium.
- The Huygens' Principle
-
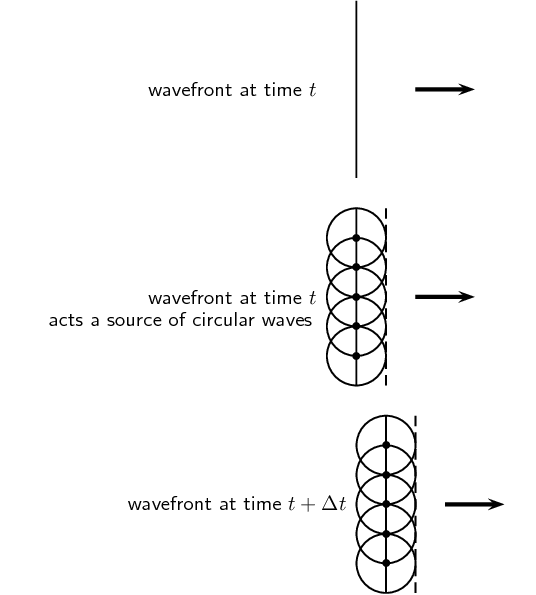
Every point of a wave front serves as a point source of spherical, secondary waves. After a time t, the new position of the wave front will be that of a surface tangent to the secondary waves.
Huygens' principle applies to any wavefront, even those that are curved as you would get from a single point source. A simple example of the Huygens' Principle is to consider the single wavefront in Figure 6.2.
Worked example 1: Application of the Huygens' principle
Given the wavefront,
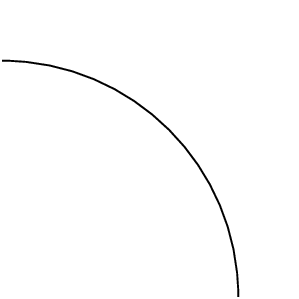
use the Huygens' Principle to determine the wavefront at a later time.
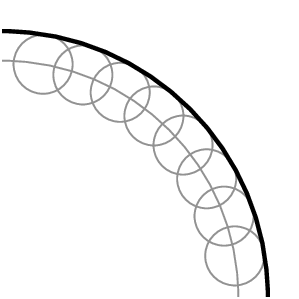
Draw circles at various points along the given wavefront

Join the circle crests to get the wavefront at a later time
|
Previous
6.2 Wavefronts
|
Table of Contents |
Next
6.4 Diffraction
|
