25.4 Platonic solids
The Platonic solids are a special group of 3D objects with faces that are congruent, regular polygons. The name of each Platonic solid comes from the number in Greek for the total number of faces it has, and “hedron”, which means “face”.
- Tetrahedron: An object with four congruent faces. Each face is an equilateral triangle. The prefix tetra- means four.
Максим Пе, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Hexahedron: (also called a cube) is an object with six congruent faces. Each face is a square. The prefix hexa- means six.
Максим Пе, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Octahedron: an object with eight congruent faces. Each face is an equilateral triangle. The prefix octa- means eight.
Максим Пе, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Dodecahedron: an object with twelve congruent faces. Each face is a regular pentagon. The prefix dodeca- means twelve.
Максим Пе, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Icosahedron: an object with twenty congruent faces. Each face is an equilateral triangle. The prefix icosa- means twenty.
Максим Пе, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Worked Example 25.2: Classify different objects
Identify the objects \(A\) to \(G\).
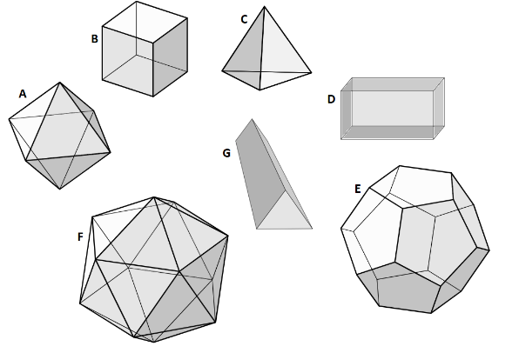
Use your knowledge of 3D objects to identify each solid.
- Object A: Octahedron
- Object B: Hexahedron or cube
- Object C: Tetrahedron
- Object D: Rectangular prism or cuboid
- Object E: Dodecahedron
- Object F: Icosahedron
- Object G: Triangular prism
