6.6 Summary
|
Previous
6.5 Area, sine, and cosine rules
|
Next
End of chapter exercises
|
6.6 Summary (EMBHT)
|
square identity |
quotient identity |
| \(\cos^2\theta + \sin^2\theta = 1\) | \(\tan\theta = \dfrac{\sin\theta}{\cos\theta}\) |
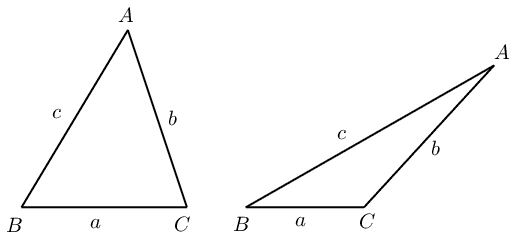
|
negative angles |
periodicity identities |
co-function identities |
| \(\sin (-\theta) = - \sin \theta\) | \(\sin (\theta \pm \text{360}\text{°}) = \sin \theta\) | \(\sin (\text{90}\text{°} - \theta) = \cos \theta\) |
| \(\cos (-\theta) = \cos \theta\) | \(\cos (\theta \pm \text{360}\text{°}) = \cos \theta\) | \(\cos (\text{90}\text{°} - \theta) = \sin \theta\) |
|
sine rule |
area rule |
cosine rule |
| \(\frac{\sin A}{a} = \frac{\sin B}{b} = \frac{\sin C}{c}\) | area \(\triangle ABC = \frac{1}{2} bc \sin A\) | \(a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2 bc \cos A\) |
| \(\frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C}\) | area \(\triangle ABC = \frac{1}{2} ac \sin B\) | \(b^2 = a^2 + c^2 - 2 ac \cos B\) |
| area \(\triangle ABC = \frac{1}{2} ab \sin C\) | \(c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2 ab \cos C\) |
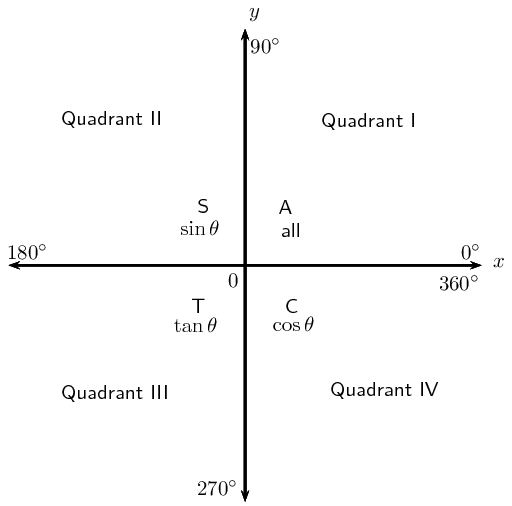
General solution:
- \begin{align*} \text{If } \sin \theta &= x \\ \theta &= \sin^{-1}x + k \cdot \text{360}\text{°} \\ \text{or } \theta &= \left( \text{180}\text{°} - \sin^{-1}x \right) + k \cdot \text{360}\text{°} \end{align*}
- \begin{align*} \text{If } \cos \theta &= x \\ \theta &= \cos^{-1}x + k \cdot \text{360}\text{°} \\ \text{or } \theta &= \left( \text{360}\text{°} - \cos^{-1}x \right) + k \cdot \text{360}\text{°} \end{align*}
- \begin{align*}
\text{If } \tan \theta &= x \\
\theta &= \tan^{-1}x + k \cdot \text{180}\text{°}
\end{align*}
for \(k \in \mathbb{Z}\).
How to determine which rule to use:
-
Area rule:
- no perpendicular height is given
-
Sine rule:
- no right angle is given
- two sides and an angle are given (not the included angle)
- two angles and a side are given
-
Cosine rule:
- no right angle is given
- two sides and the included angle angle are given
- three sides are given
|
Previous
6.5 Area, sine, and cosine rules
|
Table of Contents |
Next
End of chapter exercises
|
