1.2 The real number system
|
Previous
1.1 Introduction
|
Next
1.3 Rational and irrational numbers
|
1.2 The real number system (EMA3)
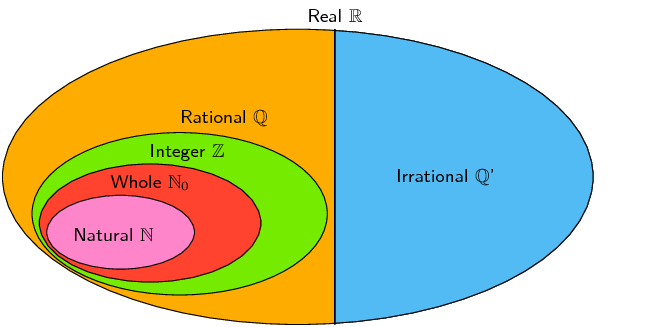
We use the following definitions:
-
\(\mathbb{N}\): natural numbers are \(\left\{1; 2; 3; \ldots\right\}\)
-
\(\mathbb{N}_0\): whole numbers are \(\left\{0; 1; 2; 3; \ldots\right\}\)
-
\(\mathbb{Z}\): integers are \(\left\{\ldots; -3; -2; -1; 0; 1; 2; 3; \ldots\right\}\)
The following video shows an example of determining which of the above sets of numbers a particular number is in.
Not all numbers are real numbers. The square root of a negative number is called a non-real or imaginary number. For example \(\sqrt{-1}\), \(\sqrt{-28}\) and \(\sqrt{-5}\) are all non-real numbers.
|
Previous
1.1 Introduction
|
Table of Contents |
Next
1.3 Rational and irrational numbers
|
